- Blog
Achilles Tendinitis Treatments
Posted on 01-28-2026 in Achilles Tendinitis by Dr. Erik Nilssen

Posted on 01-28-2026 in Achilles Tendinitis by Dr. Erik Nilssen
The Achilles tendon is the largest and strongest tendon in the body, and it serves a very important purpose. It connects the gastrocnemius and soleus – the two primary calf muscles – to the back of the heel bone. When too much stress is placed on the Achilles tendon, also known as the heel cord, it tightens and becomes overworked. As a result, it can become inflamed, a condition that is known as Achilles tendinitis.
Over time, scar tissue can develop on the tendon and a tear or rupture can occur. With proper treatment, worsening of the condition can be avoided and can reduce pain so that you can continue to participate in your physical activities. There are two treatment options available for Achilles tendinitis: non-surgical and surgical.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For many people, non-surgical treatment can relieve the pain that is associated with Achilles tendinitis. There are several non-surgical treatment options available, including:
If the injury does not respond to self-treatment within two weeks, you should see an orthopedic surgeon for further evaluation.
Surgical Treatments
If the pain that is caused by Achilles tendinitis does not improve after six months of non-surgical treatments, surgery may be necessary. There are three main types of surgeries that can be done to treat the condition:
If you are suffering from Achilles tendinitis, schedule an appointment with a North Florida Bone & Joint Specialists surgeon by calling 855-998-FOOT or complete our contact form.

September is Healthy Aging Month, an observance dedicated to promoting the positive aspects of growing older and encouraging proactive steps toward maintaining long-term health. In its 33rd year, Healthy Aging Month inspires adults of all ages to focus on lifestyle habits that support vitality, independence and overall well-being.
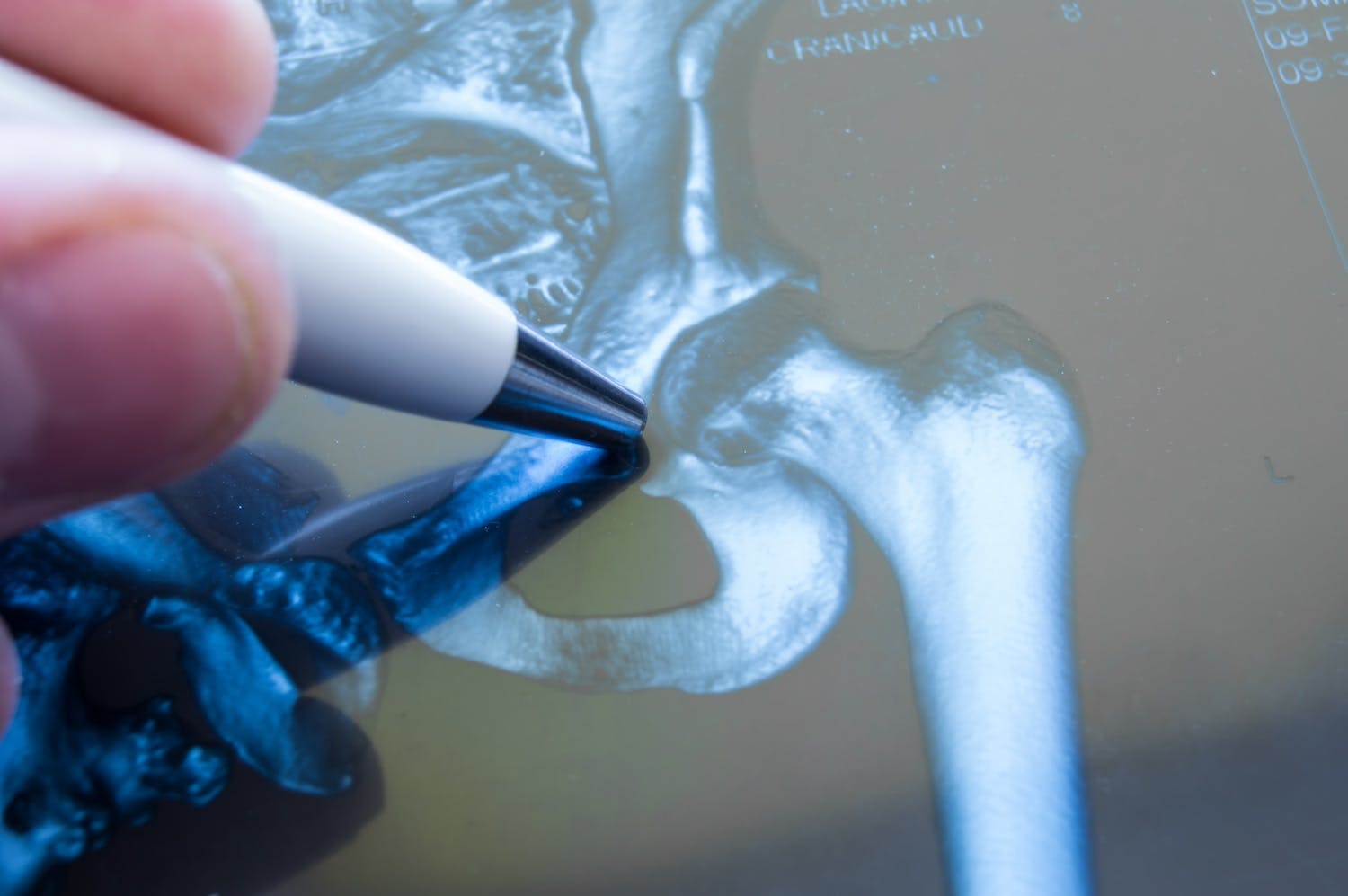
Ischiofemoral Impingement (IFI) is a lesser-known but often painful condition affecting the hip joint. This condition arises when the ischium (a bone in the pelvis) and the femur (the thigh bone) come into abnormal contact, which compresses soft tissues surrounding the hip. While the discomfort typically manifests in the buttocks or groin, particularly when moving the hip or walking, it can also present as low back pain, making it challenging to diagnose early. Additional symptoms and causes include discomfort during prolonged sitting, reduced range of motion, stiffness and/or tightness in the hip area.

May is Arthritis Awareness Month, an opportunity to increase public understanding of arthritis and its impact on millions of lives. Established by the Arthritis Foundation, this national observance highlights the importance of early diagnosis, effective treatment, and ongoing research to improve the quality of life for those with arthritis.